Intra-articular Therapies (Joint Injections)
Regenerative treatments are aimed at restoring structure and function to tissues, organs, and body systems that have been damaged by injury or disease.
Intra-articular therapies (joint injections) include the following therapies:
- Stem Cell Therapy
- PRP (platelet-rich plasma)
- HA (hyaluronic acid)
- Steroids, anti-inflammatories
Platelet Replacement Therapy
Platelet Replacement Therapy takes advantage of the anti-inflammatory properties of platelets. Following an injury, an immediate inflammatory response is evident by the heat and swelling noted at the injured site.
Inflammation is essential to stopping the spread of infection and allowing the transport of inflammatory cells to the injury site. However, healing cannot take place until the inflammatory response stops.
Platelets signal the white blood cells to help clean up the inflammation and release growth factors. This process ultimately inhibits inflammation and allows the recovery process to begin.
With many chronic conditions, the injured site remains in a perpetual state of inflammation, thereby impeding the healing process. Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) jump-starts the recovery process by converting the injury from a site of inflammation to one of recovery.
How Is Platelet-Rich Plasma Acquired?
PRP is harvested directly from a small sample of the patient’s blood and is ready for use within 15 minutes. These treatments are advantageous because they can be made available for treatment relatively quickly. In addition, they are derived from the patient’s own blood, eliminating the risk of an inflammatory reaction response.
What Types of Injuries or Diseases Would Benefit from PRP treatment?
PRP commonly treats soft tissue injuries (cartilage, tendons, ligaments), arthritis, joint pain, and wounds.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells can be harvested from various tissues, including skin, adipose (fat), and bone marrow. The fat-derived stem cells are simple to retrieve, have a higher concentration than bone marrow, and have shown a mix of “regenerative” cells. In the correct environment, these stem cells can be transformed into numerous cell types, including bone, cartilage, skin, nerves, and muscles.
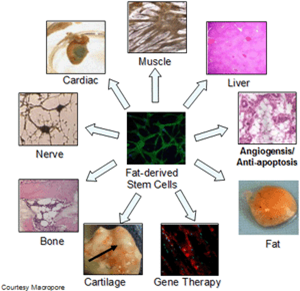
Stem cell harvesting is a three-step process:
Step 1: A Vet-Stem credentialed veterinarian collects the fat from your pet.
Step 2: The fat is sent to a lab specializing in stem cell harvesting, where the cells are isolated and grown in a cultured medium.
Step 3: The cells are shipped directly back to your veterinarian, where they are injected into the injured area.
How Does Stem Cell Therapy Promote Healing?
The stem cells work through three mechanisms when present in an inflammatory environment.
First: the cells demonstrate regenerative capacity by differentiating into the cell line of interest, such as bone, cartilage, or muscle cells.
Second: the cells support healing by releasing growth factors and cytokines that stimulate blood flow and tissue remodeling while slowing down cell death.
Finally: the stem cells act as a homing beacon, drawing circulating stem cells to the injured site. In addition, the injected stem cells can migrate to areas of inflammation, allowing for a targeted approach to healing.
What Types of Diseases or Injuries Would Benefit From Stem Cell Therapy?
Numerous studies have shown stem cells to demonstrate efficacy in arthritis, tendon repair, fractures, ligament damage, and chronic wounds. There is active research looking at using stem cells to treat liver disease, cardiac disease, and renal disease.